Hydraulic Thumb Size Details

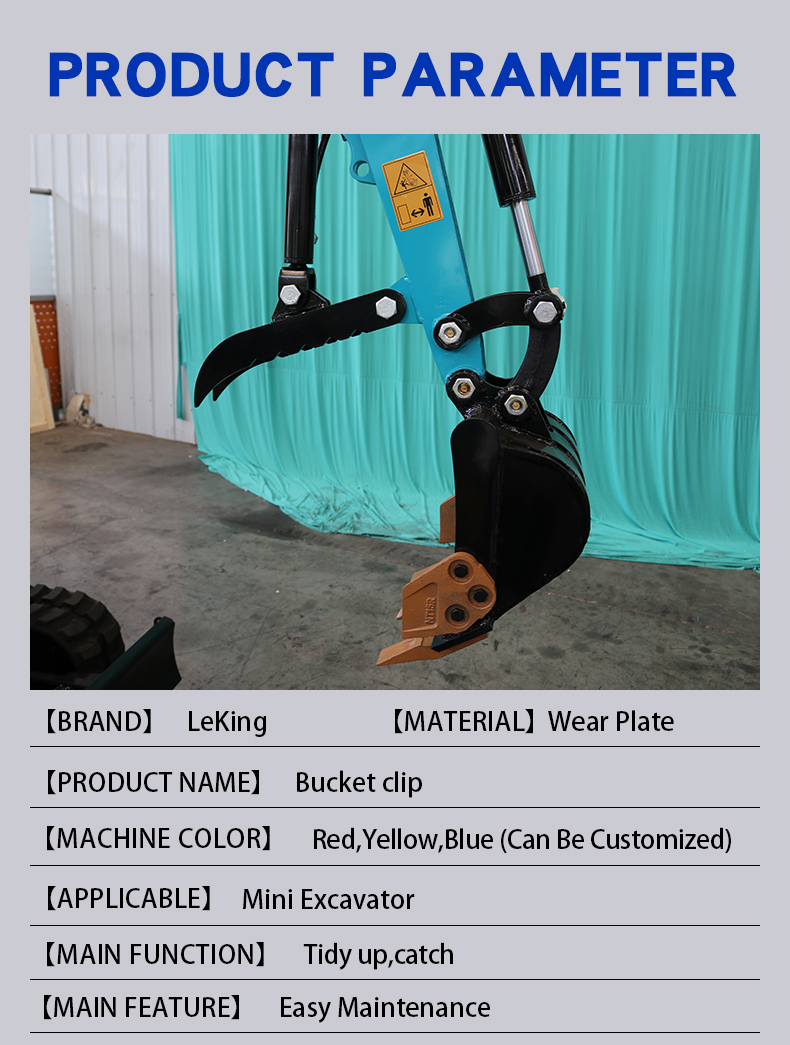







In order to meet the different needs during construction, people put forward higher requirements for the functions of Mini excavators. In addition to the conventional excavation functions, the current Mini excavators also have additional grabbing functions; at the same time, when the bucket is excavating , the material is easy to fall when the bucket is excavating, resulting in low excavation efficiency; therefore, on the basis of traditional excavators, a Thumb is often set under the bucket, and the Thumb cooperates with the bucket to play a clamping role.
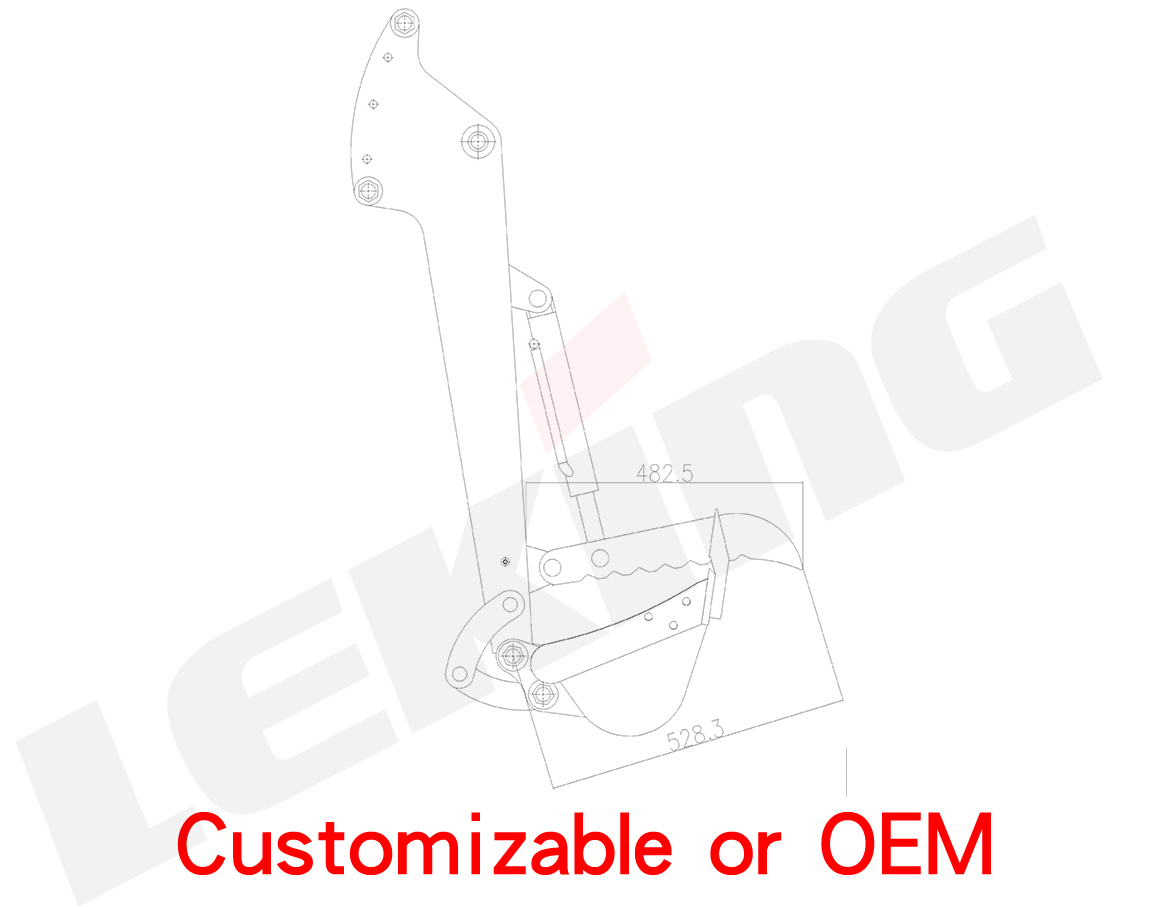
The ordinary Thumb rotates by itself, and at the same time uses the latch to fix the Thumb and the stick relatively, so that the Thumb can be folded and stored or worked; The shaft hole corresponds to the front end hole of the three-hole lug plate. Insert the pin to fix the Thumb. At this time, the Thumb is in working state; when the Thumb is not in use, unplug the pin and rotate the Thumb around the middle axis to the three-hole lug. At the rear end of the plate, insert the pin shaft into the pin shaft hole and the rear end hole of the three-hole lug plate to fix the Thumb. At this time, the Thumb is in a retracted state and will not affect the normal excavation operation; however, the structure of this Thumb is relatively It is relatively simple, and the applicable construction scenarios are limited.
Another existing Thumb is mostly installed on the bucket or stick and driven by an independent hydraulic pressure; this hydraulic Thumb controls the expansion and contraction of the piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder, so that the clamp swings relative to the bucket of the excavator. The action of clamping the material can be formed; when not in use, the piston rod of the control hydraulic cylinder is kept in a retracted state, so that the clamp is attached to the side of the boom of the excavator, which does not affect the normal excavation of the excavator; when necessary When the bucket is used, the tipper cylinder drives the piston rod to extend, and the bucket rotates through the four-bar linkage mechanism; at the same time, the recovery cylinder drives the piston rod to extend, so that the bucket also starts to rotate toward the bucket to achieve clamping.